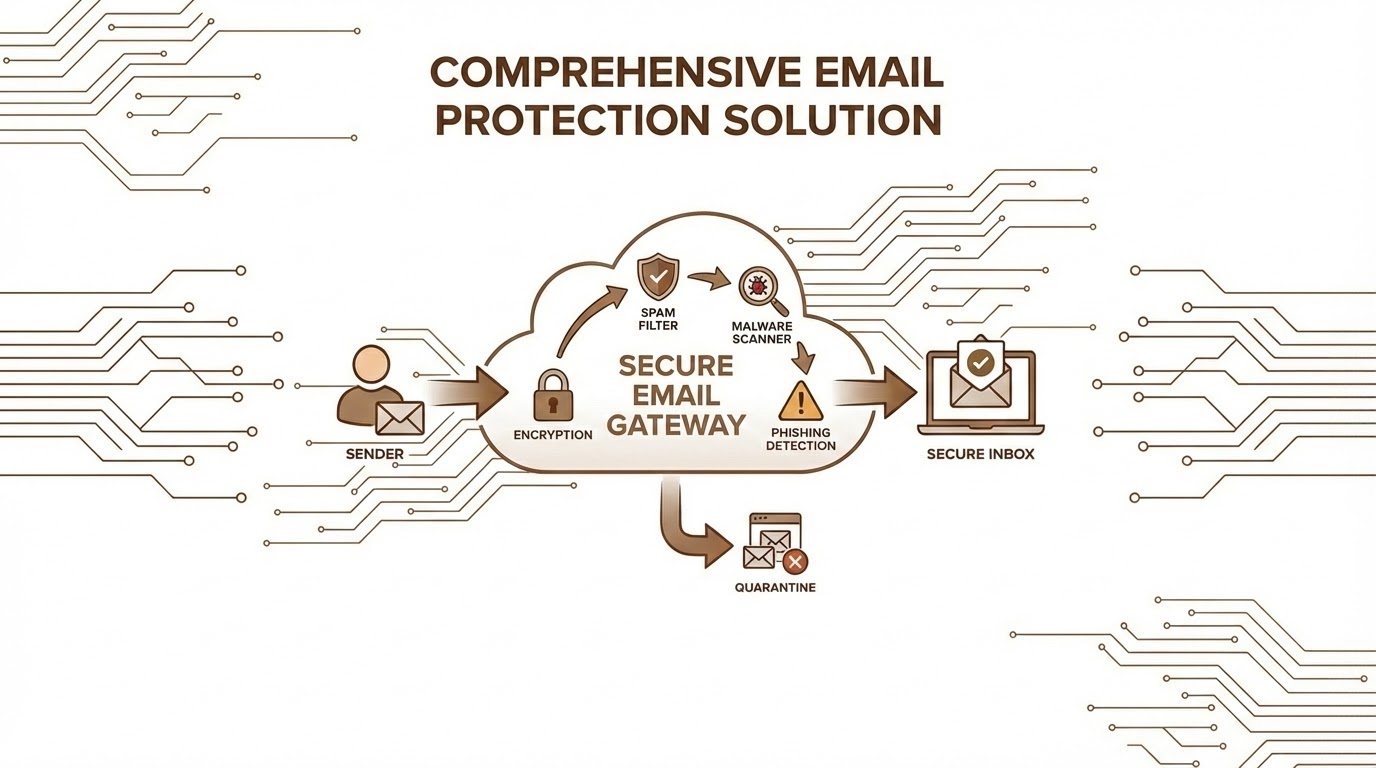
Email cybersecurity focuses on protecting email communications from threats like phishing, malware, and unauthorized access. Here are the key points:
Common Threats
- Phishing: Deceptive emails tricking users into revealing personal information.
- Spear Phishing: Targeted attacks using personal information to appear legitimate.
- Ransomware: Malicious software delivered via email that encrypts files for ransom.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC): Fraud where attackers impersonate trusted figures to steal money or data.
Best Practices
- Strong Passwords: Use complex passwords and change them regularly.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security.
- Caution with Links/Attachments: Verify senders and avoid suspicious content.
- Email Encryption: Protect sensitive information in transit.
Tools
- Spam Filters: Reduce phishing and malicious emails.
- Email Authentication Protocols: Use SPF, DKIM, and DMARC to verify sender authenticity.
- Antivirus Software: Scan emails for threats.
User Education
- Provide training on identifying phishing and safe email practices.
- Encourage reporting of suspicious emails.
Incident Response
- Have a plan for addressing email security breaches.
By implementing these measures, organizations can significantly enhance their email security and safeguard sensitive information.