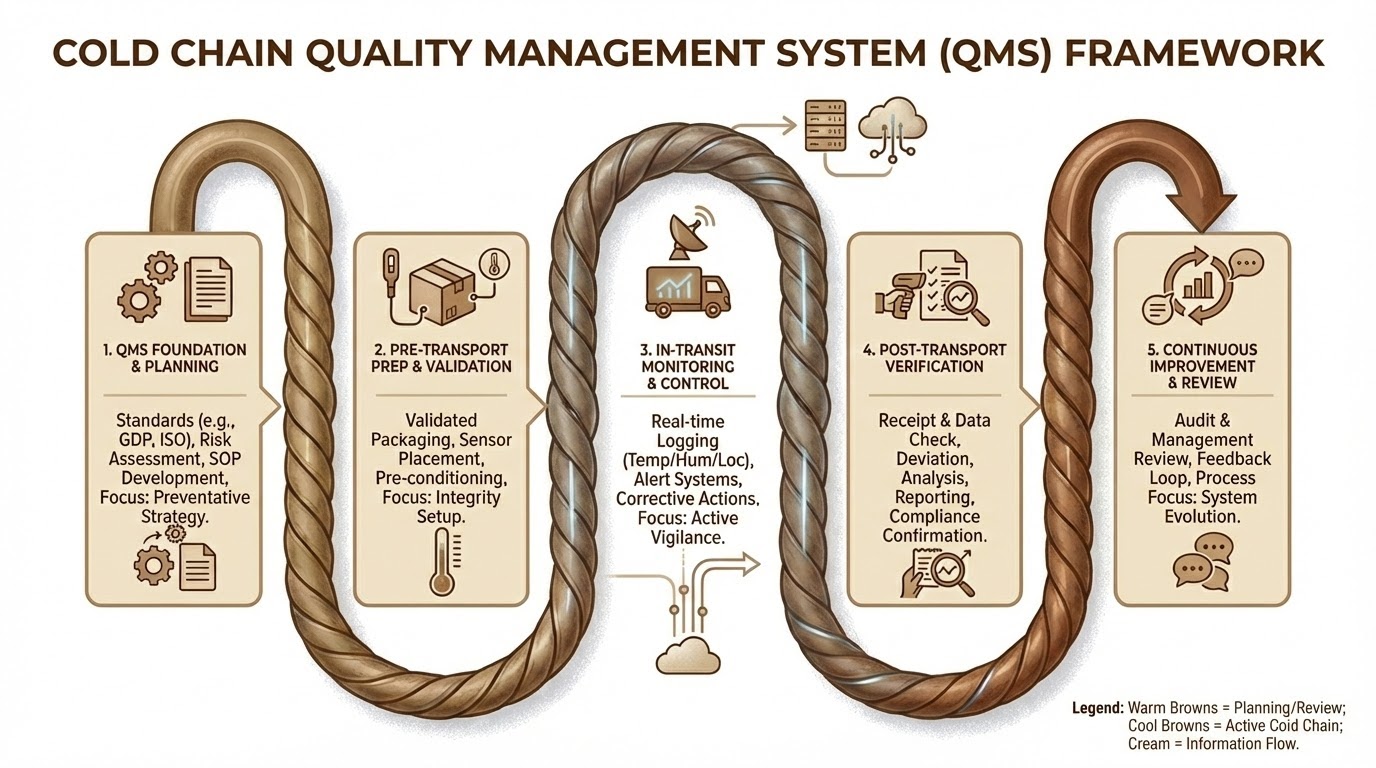
A Quality Management System (QMS) is a structured framework of policies, processes, and procedures that organizations implement to ensure they consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements, and improve their overall performance. The goal of a QMS is to enhance product or service quality and streamline operational efficiency.
Key components of a QMS typically include:
1. Quality Policy: A formal statement that sets out the organization's commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
2. Quality Planning: The process of defining quality objectives, and determining the resources and processes needed to achieve them.
3. Quality Control (QC): Activities that monitor and regulate the quality of outputs, ensuring they meet specified standards and are free from defects.
4. Quality Assurance (QA): A proactive approach to ensure quality by implementing standards, guidelines, and systematic checks to prevent issues before they arise.
5. Continuous Improvement: A process of regularly reviewing and refining systems, processes, and practices to increase efficiency, reduce waste, and improve quality.
6. Document Control: Ensures that all quality-related documentation is up-to-date, accurate, and accessible to relevant stakeholders.
7. Internal Audits and Reviews: Regular assessments of processes to identify areas for improvement and ensure compliance with the QMS.
By applying a QMS, organizations aim to boost customer satisfaction, improve consistency, and achieve better overall business performance.