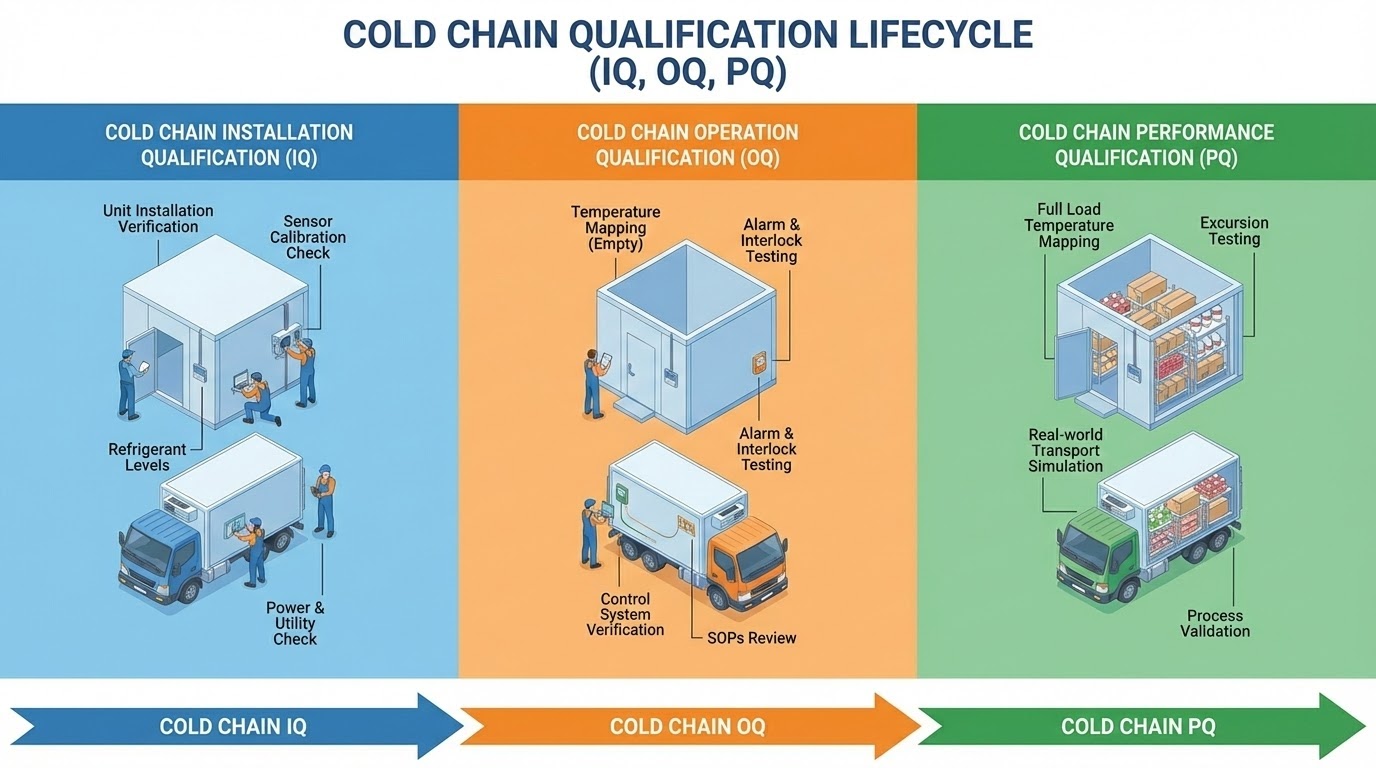
IQ, OQ, and PQ are terms used in validation processes,particularly in industries like pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, and manufacturing,to ensure that equipment, systems, or processes perform as intended. These terms refer to different stages of the validation lifecycle.
1. IQ (Installation Qualification)
- Purpose: Ensures that equipment or systems are installed correctly according to the manufacturer's specifications and regulatory requirements.
- Focus: Verifies that the equipment is installed in the right location, is properly configured, and has the necessary utilities and support (e.g., power, cooling, ventilation).
- Key Activities:
- Checking the installation location and environment.
- Verifying equipment and system components.
- Confirming that installation procedures are followed.
- Ensuring that safety features are in place.
2. OQ (Operational Qualification)
- Purpose: Verifies that the equipment or system operates according to its design specifications within the defined operating ranges.
- Focus: Ensures that the system operates correctly in all modes (startup, operation, shutdown) and meets predefined performance standards.
- Key Activities:
- Testing equipment under normal and extreme conditions.
- Verifying functionality (e.g., speed, temperature, pressure, flow rates).
- Ensuring that all system controls, alarms, and interlocks function properly.
- Performing tests to validate that the system can handle a variety of operational conditions without failure.
3. PQ (Performance Qualification)
- Purpose: Confirms that the equipment or system performs consistently and reliably under normal working conditions over a period of time.
- Focus: Ensures that the equipment/system will continue to perform as expected in actual production or use settings.
- Key Activities:
- Running the system under real-life, operational conditions (e.g., in actual production runs or tests).
- Monitoring performance to ensure it meets quality standards.
- Documenting results to demonstrate that the equipment consistently produces desired outcomes.
- Ensuring that processes remain within acceptable limits during routine use.
These validation stages are critical to maintaining quality, safety, and compliance, especially in highly regulated industries.